The Module System
Each module's table includes the following columns:
- ID (see next page)
- Text columns
- Numerical columns (mostly used for specific measurement)
- Limited selection columns (enums, lookup columns, specific column values, or booleans)
Less commonly-used partitionable properties were store externally in the [module]_tags and [module]_tag_groups tables and are made available via pivot tables.
In the case of sparsely-used numeric measurements, optional numeric properties (onps) were stored externally in the [module]_onps tables.
The basic database schema to accomodate for this design is therefore (lithics example):
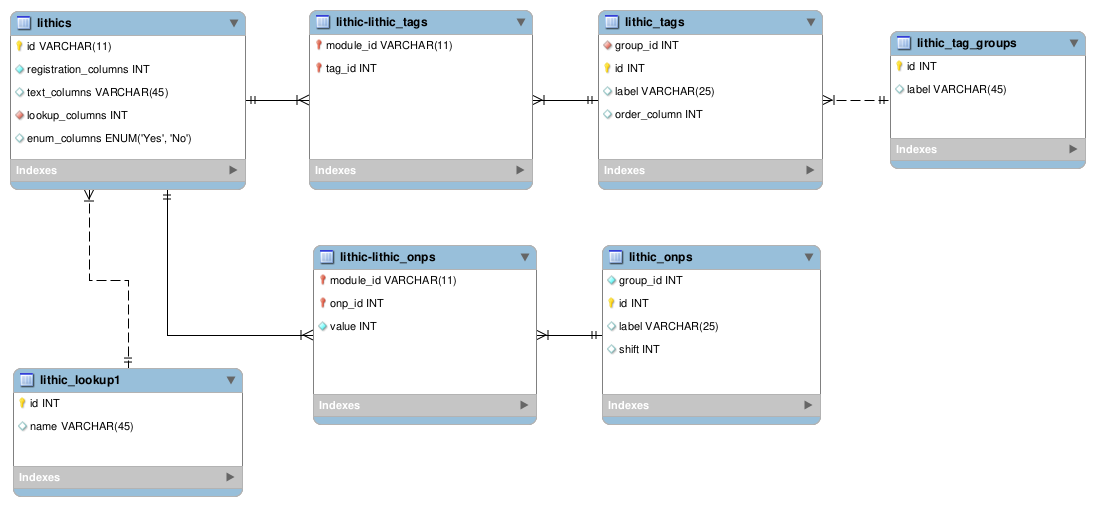
At the (back end) application level, each module has its set of configuration files, Request Forms (Laravel's Validation), and Models (Laravel's ORM classes). In addition, module-agnostic Request Forms, Controllers, and Services are located in the standard Laravel application folders. Module agnostic API endpoints serve as the gateway to these components.
This design enables flexibility with regard to each modules' specific details in a module-agnostic framework that is easier to maintain. It also allows for a relatively easy incorporation of new modules into the project.